Generator Size Guide: 7 Powerful Tips to Find Out How Many Watts You Really Need for Your Home
How Many Watts Generator Do I Need for My House?
Introduction
Power outages can strike at any time, and when they do, having the right generator can make all the difference. But the real question most homeowners ask is, “How many watts generator do I need for my house?” Choosing the right size generator isn’t just about convenience—it’s about safety, efficiency, and making sure your essential appliances stay powered during blackouts.

The good news is that figuring this out doesn’t have to be complicated. With a simple “how many watts generator do I need for my house calculator”, you can estimate your power needs based on the appliances and systems you plan to run. Whether it’s keeping the lights on, powering your refrigerator, or running your heating and cooling systems, calculating wattage correctly ensures you invest in the right generator for your lifestyle and budget.
If you’ve ever faced a sudden power outage, you already know the importance of having a reliable generator. But here’s the big question: how many watts generator do I need for my house? The answer depends on your energy usage, the size of your home, and the number of appliances you want to run. In this guide, we’ll break everything down step by step so you can choose the right generator without confusion.
Why Generator Wattage Matters
When it comes to backup power, the wattage of your generator is one of the most important factors to consider. If you don’t choose the right size, your generator may either fail to handle essential appliances or you might end up spending more money than necessary on a unit that’s too large for your needs.

For example, many homeowners ask, “What size generator to run a 1,500 sq ft house?” The answer depends on what you plan to power—basic lights and a refrigerator will need far less wattage compared to running central air conditioning and multiple large appliances at the same time.
The bottom line is that the wattage determines how comfortable and functional your home will be during an outage. Understanding the right balance helps you get a reliable generator that meets your energy needs without overspending.
The wattage of a generator determines how many appliances and devices it can run at the same time. If you choose a generator with too little power, it may trip or fail when larger appliances like refrigerators or air conditioners start up. On the other hand, going too big may mean overspending on something you don’t really need.
Running Watts Explained
Running watts are the continuous power a generator can provide. This is the steady power your appliances use once they are up and running.
Starting Watts and Why They Matter
Some appliances, like refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners, need an extra surge of power when starting. This temporary boost is called starting watts, and your generator must be able to handle it.
Factors That Decide Generator Size for Your Home
When figuring out the right generator size, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer. Every home has different power needs, and the generator you choose should match those needs. Some key factors include the number of appliances you want to run, the square footage of your home, and whether you need backup power for just essentials or the entire house.
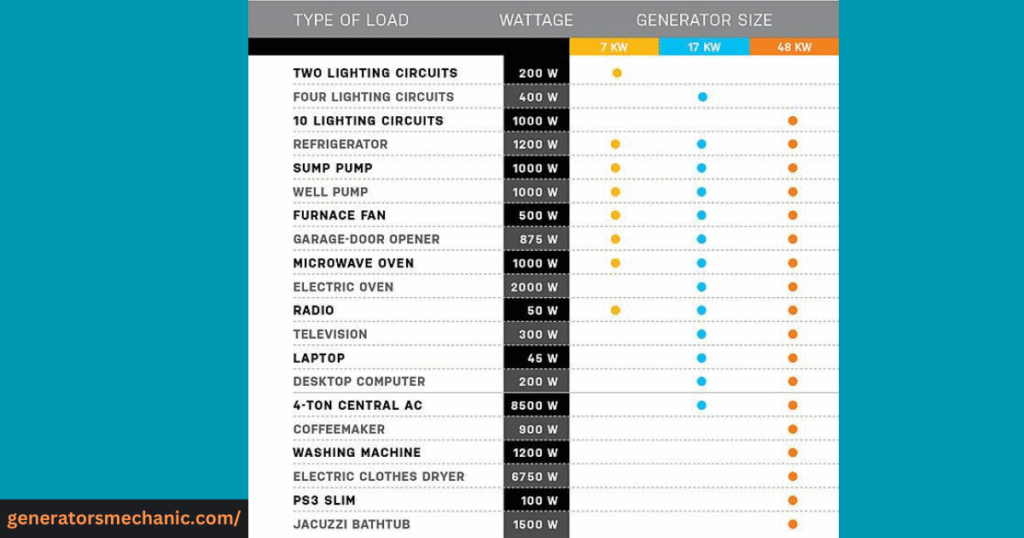
Many homeowners also search for tools like a “what size generator do I need for my house calculator” to get a quick estimate. These calculators can be helpful, but the most reliable way is to list out your essential appliances, check their running and starting wattages, and add them up. For example, powering a refrigerator, a few lights, and a TV will require far less wattage than running central air conditioning, water heaters, and multiple large appliances together.
Ultimately, your lifestyle, budget, and energy priorities play a big role. If you only need to keep the basics on during an outage, a smaller portable generator might do the job. But if you want full-home comfort without compromise, a larger standby generator may be the best choice.
Several things influence how many watts your home generator should have:
- Number of Appliances – The more devices you want to power, the higher the wattage required.
- House Size – Larger homes with multiple rooms usually need more wattage to keep lights and major appliances running.
- Power Outage Frequency – If blackouts are rare, a smaller generator may be enough. If frequent, a whole-house generator could be worth it.
- Budget and Fuel Type – Higher wattage generators cost more and consume more fuel, so balance your needs with your budget.
How to Calculate the Right Wattage for Your House
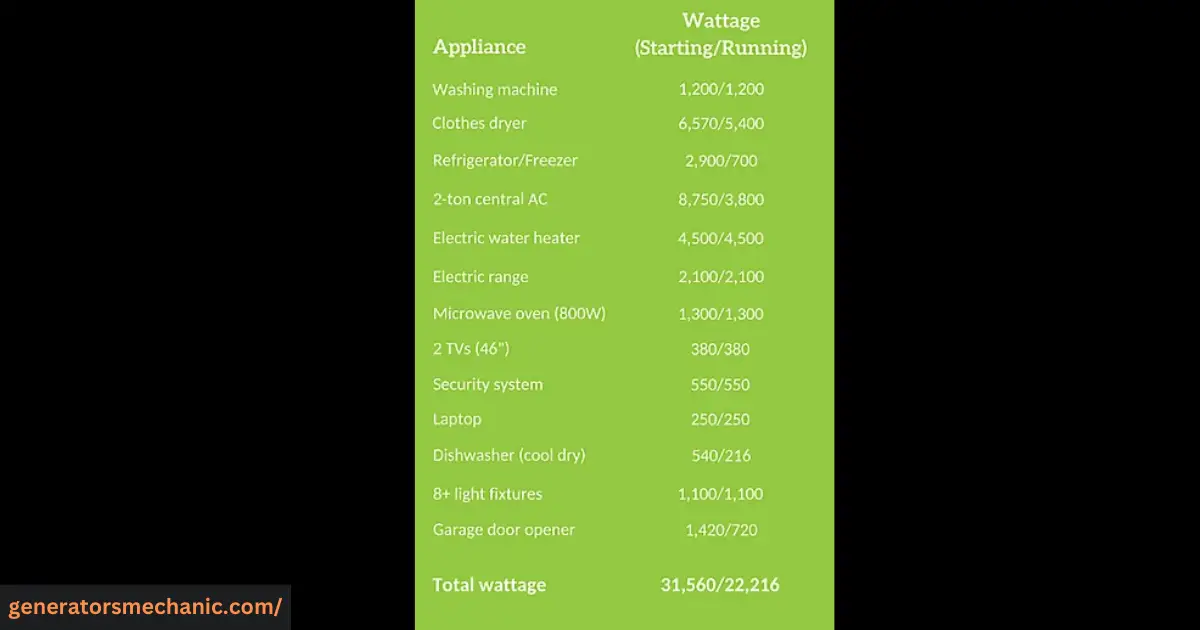
Choosing the correct generator size starts with understanding your home’s total power needs. The best way is to list out all the appliances and devices you want to run during a power outage—like lights, refrigerator, air conditioner, sump pump, or TV—and note down their wattage.
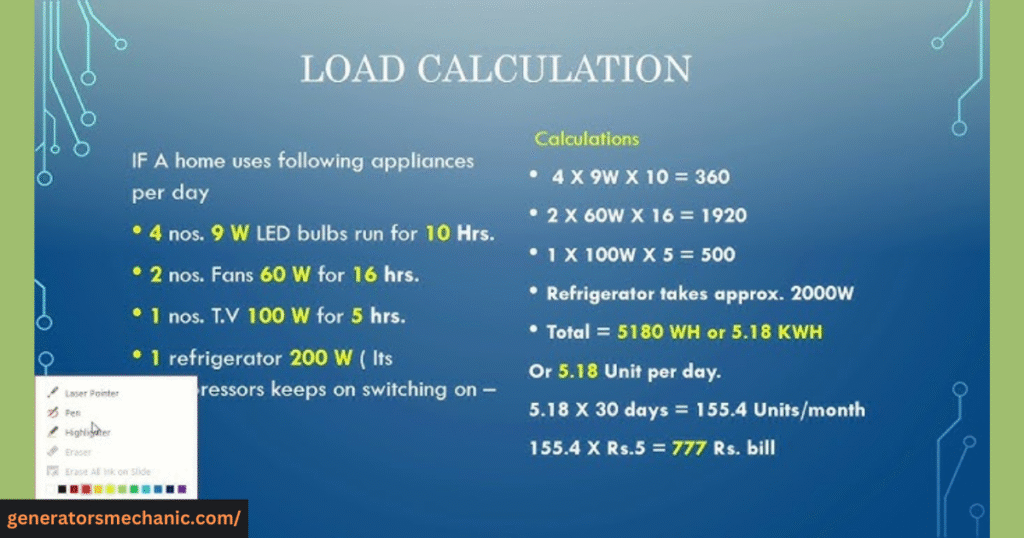
Add up the running watts for each item and then include the highest starting watt requirement. This final number gives you the minimum wattage your generator must handle safely.
For homeowners who want a quicker approach, using a generator sizing calculator can make things much easier. These online tools let you select appliances from a checklist, and they automatically calculate the recommended generator size for your house. Whether you do the math manually or rely on a calculator, the goal is the same: ensuring your generator can handle both everyday usage and sudden power surges without overload.
Choosing the right generator starts with a little math.
- Make a list of all appliances you want to power.
- Note their running wattages.
- Add the total running watts.
- Add the highest starting watt to the total.
This will give you the minimum wattage your generator should provide.
Example for a Small Home (1,000–3,000 sq. ft.)
A small home running essentials like lights, fans, a refrigerator, and a TV may only need 3,000–5,000 watts.
Example for a Medium to Large Home
A medium home running appliances like refrigerators, sump pumps, heaters, and a small AC may need 5,000–8,000 watts.
Example for Whole-House Backup Generators
For large homes with central air, electric water heaters, and multiple appliances, you may need 10,000–20,000+ watts with a standby generator.
Recommended Generator Sizes for Common Household Needs

Choosing the right generator becomes easier when you match it to your household setup. For example, many people ask, “What size generator do I need for a 3-bedroom house?” The answer depends on what appliances you want to keep running.
A typical 3-bedroom home with essentials like lights, fans, a refrigerator, and maybe a small air conditioner may require around 5,000 to 7,500 watts. If you also want to power larger appliances like a central air system, water heater, or multiple electronics at the same time, you may need a generator in the 10,000–12,000-watt range.
As a quick rule of thumb:
· Small homes or apartments → 3,000–5,000 watts (basic appliances only)
· 3-bedroom house with essential appliances → 5,000–7,500 watts
· Whole-house backup for larger homes → 10,000–20,000 watts
By understanding these ranges, you can confidently choose a generator that fits your daily needs without overspending on unnecessary power.
Here’s a quick guide for common scenarios:
- Refrigerator + Lights + TV + Small Appliances → 3,000–4,000 watts
- Add a Window AC or Sump Pump → 5,000–7,000 watts
- Central AC + Multiple Large Appliances → 10,000–15,000 watts
- Whole-House Backup (everything at once) → 15,000–25,000 watts
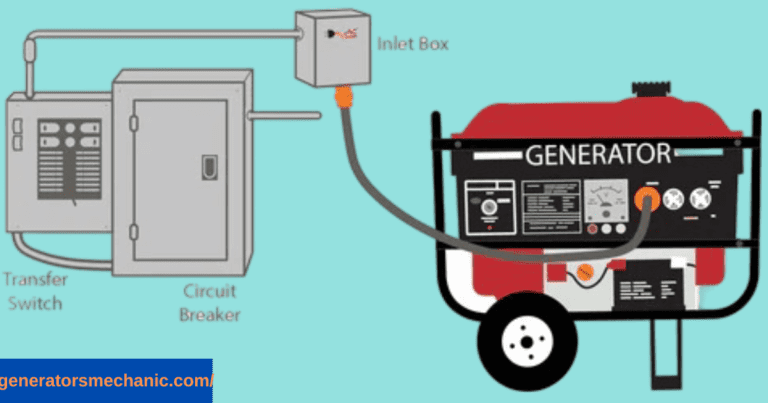
Portable vs Standby Generators – Which is Better for You?
When choosing a generator for your home, one of the biggest decisions is whether to go with a portable generator or invest in a standby generator. Portable generators are more affordable, easy to move around, and work well if you only need to power a few essential appliances during an outage. They usually range from 2,000 to 10,000 watts, making them a good option for smaller or temporary needs.
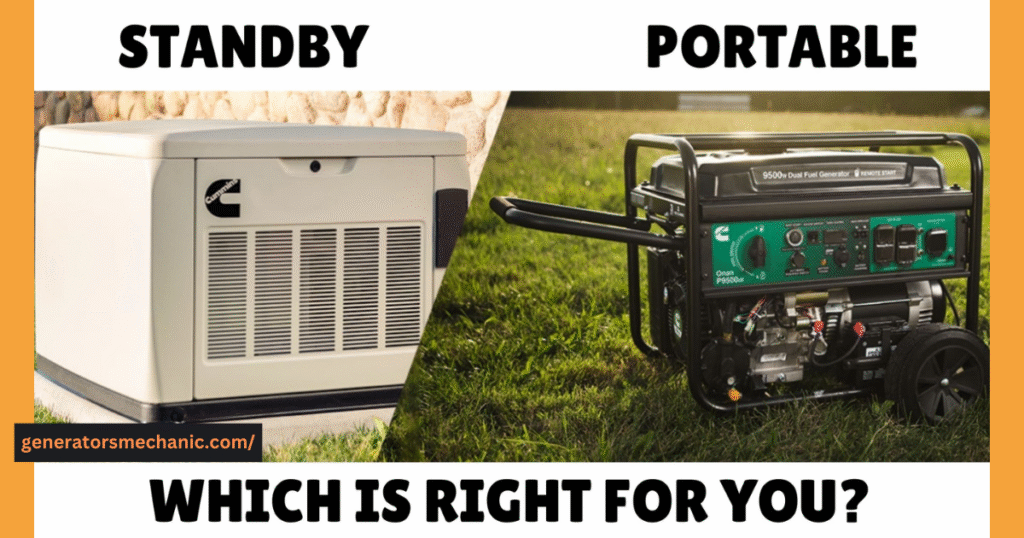
On the other hand, standby generators are permanently installed and can power your entire home automatically when the electricity goes out. These units are designed for higher wattage, with some models even reaching the capacity of a 25,000-watt generator, which is powerful enough to handle large homes, central air conditioning systems, and multiple heavy appliances at the same time.
If you experience frequent outages or want peace of mind that your whole home will stay powered without lifting a finger, a standby generator may be the better investment. But if you only need backup for a few essentials and want to stay within budget, a portable generator will get the job done.
- Portable Generators are cheaper, easier to move, and good for short outages or running a few appliances. Typically range between 2,000–10,000 watts.
- Standby Generators are permanently installed, start automatically, and can power the entire house. They range from 7,000 watts up to 25,000+ watts.
Cost Considerations When Choosing a Generator
When buying a generator, it’s not just about the power—it’s also about the cost. Larger generators with higher wattage can easily power more appliances, but they also come with a bigger price tag and higher fuel consumption. Installation, maintenance, and fuel type (gas, propane, or diesel) all add to the total expense.

One of the most common questions homeowners ask is, “What size generator do I need for a 2,500 square foot house?” The answer depends on how many appliances and systems you want to run. For a home this size, you might need anywhere between 7,500 to 12,500 watts, which could cost more upfront but ensures comfort during outages. The key is to balance your budget with your actual energy needs so you don’t end up overpaying for unnecessary power.
The higher the wattage, the more expensive the generator. Portable units may cost anywhere from $500–$2,500, while standby systems can range from $3,000–$10,000+, depending on size and installation. Also, remember that fuel consumption increases with wattage, so think about your long-term budget.
Final Thoughts
So, how many watts generator do I need for my house? The answer depends on your home size, essential appliances, and lifestyle. Smaller homes can get by with 3,000–5,000 watts, while larger households may require 10,000+ watts for whole-home coverage. The best approach is to calculate your exact needs and then choose a generator slightly above that capacity to ensure safety and reliability.
FAQs
How many watts generator do I need for a 2,000 sq ft house?
A 2,000 sq ft home usually needs 5,000–7,500 watts, depending on the number of appliances.
What size generator is needed to run an AC and a refrigerator together?
At least 5,000–6,500 watts is recommended to safely run both.
Is a 10,000-watt generator enough for a house?
Yes, for most medium to large homes, a 10,000-watt generator is enough to cover essentials and some luxury appliances.
How do I calculate the exact wattage for my house?
Add the running watts of all appliances you want to power, then add the highest starting watt requirement.
How many watts Generator to run an entire home?
A generator with a capacity of 5,000 watts can sufficiently power essential items such as lights, a refrigerator, and a freezer. In contrast, a 15,000-watt generator offers a more comfortable experience by powering lights, a refrigerator, a freezer, central air conditioning, a water heater, an oven or stove, a microwave, and a television.
How do I calculate what size generator I need for my house?
To calculate the right generator size for your home, start by listing the essential appliances and systems you want to run during a power outage. Check the wattage requirements for each item—this information is usually found on the label or in the user manual.
Add up all the running watts (the continuous power needed) and then include the highest starting watts (the extra power required when certain appliances like refrigerators or air conditioners first turn on).
For example, if your fridge needs 700 running watts and 2,000 starting watts, and your lights, fans, and TV total 1,500 watts, your generator should handle at least 3,500 watts.
To be safe, choose a generator that provides a little more power than your calculation, so you don’t overload it and you have room for unexpected usage.
In short, the formula is:
Total Running Watts + Highest Starting Watt = Minimum Generator Size You Need.
How many watts for a 2000 sq ft house?
For a house measuring 2,000 square feet, a generator with a capacity of 15,000 watts is advisable to effectively power essential appliances and systems. This size of generator guarantees dependable backup for the critical needs of most homes.
How big a generator do I need to run my whole house?
12,000 to 22,000 watts
To power an entire home, a significantly larger generator is necessary, typically ranging from 12,000 to 22,000 watts (12kW – 22kW) or more, which largely depends on the size of your air conditioning unit.
How many watts does a fridge use on a generator?
Different appliances have varying wattage requirements. For instance, a refrigerator or freezer requires approximately 1,800 starting watts and 180 watts for normal operation. A portable radio consumes between 5 watts and 45 watts.