Can you charge an electric car with a generator?
Charging electric car with generator is becoming a practical solution for EV owners who need power in remote areas or during outages.
While most people rely on public charging stations or home wall units, a portable or standby generator can offer the flexibility to charge on the go.
The key is ensuring the generator has the correct wattage output and compatible connections for safe EV charging.For longer trips or off-grid living, some drivers prefer a diesel generator for EV charging, thanks to its efficiency and long runtime.
Whether it’s a compact inverter model for occasional use or a heavy-duty diesel unit for extended power, having a generator as a backup means your EV stays ready to roll, even when the grid isn’t..

The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), enacted by the U.S. Congress and approved by the White House in November 2021, dedicates $7 billion to expand, upgrade, and modernize the national electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure across the United States, ensuring broader access to fast and reliable EV charging stations.
This federal investment is part of a nationwide initiative to make EV charging stations more ko accessible, affordable, and dependable for drivers across the United States.
By reinforcing the national electric vehicle charging infrastructure, the program aims to build a comprehensive network of fast chargers that allows EV owners to charge their vehicles conveniently—whether at home, at work, or along highways. The ultimate goal is to eliminate range anxiety and make electric mobility more practical for all Americans.
However, this goal has not been fully achieved yet, and even as the EV charging network continues to grow, many electric vehicle owners still look for backup power options to feel more secure.
They want the reassurance of knowing they can charge their EV with a generator or backup battery system in case of power outages, emergencies, or remote travel. Having a reliable off-grid charging solution ensures continuous mobility and eliminates concerns about being stranded without access to a charging station.
So, is it actually possible to charge an electric vehicle using a backup battery or an alternative power source like a generator?
The answer is yes, but the process involves several technical considerations. Factors such as power output, voltage compatibility, inverter type, and charging equipment all play crucial roles in ensuring safe and efficient EV charging. In the following sections, we’ll explain how generator-based and battery-powered EV charging works, what costs you might expect, and the challenges you may encounter when setting up a reliable off-grid charging system.
Standard Methods for Charging Your Electric Vehicle with generator:

can an electric car be charged with a portable generator? when connected with the proper charging adapters, voltage converters, and safety equipment, can deliver sufficient electrical power to recharge your electric vehicle (EV) temporarily.
While they may not fully replace dedicated EV charging stations, they’re a practical emergency charging solution that helps keep your EV running until you reach a Level 2 charger or fast-charging point.
Interestingly, some innovative electric vehicle models—such as the Chinese EVs featuring built-in generator systems or range extender technology—are designed to provide onboard charging capabilities without relying solely on public charging infrastructure.
These range-extended EVs use a small internal combustion engine or generator to recharge the battery while driving, significantly reducing range anxiety during long-distance travel.
Although these systems aren’t a full substitute for standard Level 2 or DC fast charging, they can serve as a lifesaver in remote areas or emergency situations where traditional chargers are unavailable.
For routine charging requirements, relying solely on a backup battery or generator is insufficient. To keep your vehicle prepared for travel, you will need consistent access to one of three charging options:
Level 1 Charging
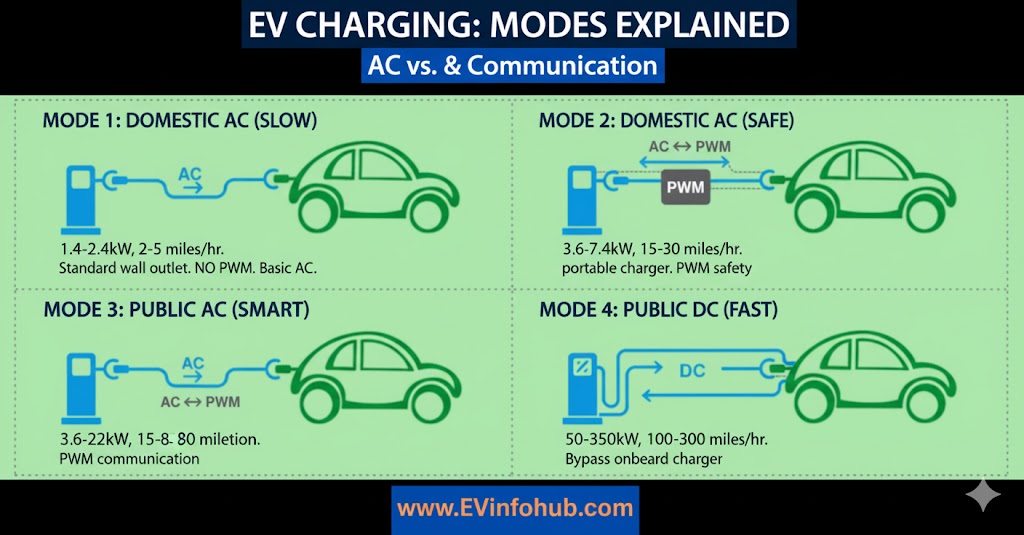
This method utilizes a standard 120-volt residential power supply. You can connect to any household outlet, provided you have a dedicated circuit to prevent power drain from other appliances. However, this method can take up to 40 hours to fully charge your vehicle, making it impractical for those who drive more than 50 miles daily without access to workplace charging.
Level 2 Fast Charging
These chargers are the most prevalent in public spaces, and many homeowners also choose to install them. Operating at 240 volts, these stations can fully charge most EVs in under five(5) hours.
can you charge an electric car with a solar generator?
Level 3 DC Fast Charging:
These chargers employ direct current (DC) to significantly expedite the charging process, but they are generally too costly and impractical for residential use.
They can completely charge an EV in approximately 30 minutes, making them suitable for businesses and charging stations located along highways. It is essential to have convenient access to charging facilities from reliable sources if you intend to own an electric vehicle.
Therefore, before arranging for backup power, ensure that the charging options available at your residence and workplace are adequate to meet your daily driving requirements.
can you charge an electric car with a generator ?
The generator must provide clean, stable power, ideally through an inverter system, to avoid damaging your EV’s sensitive charging electronics. It’s also important to match the generator’s output capacity with your EV charger’s requirements to ensure efficient and safe charging.
For those on the move, a portable generator for electric car charging can be a practical solution, especially in areas without charging stations. These compact yet powerful generators are designed to supply reliable energy for Level 1 or even some Level 2 chargers, making them ideal for road trips, camping, or emergency backup situations.
However, always follow your EV manufacturer’s guidelines and use appropriate adapters to protect both the generator and the vehicle’s battery system.

Even with an optimal charging arrangement at home, there is no absolute assurance that your vehicle will be fully charged. There remains the possibility of encountering a power outage, which could leave your electric vehicle with a depleted battery.
To prevent such an inconvenient scenario, you may be considering the option of charging your electric vehicle with a backup battery or generator. While this is feasible, there are several challenges to address.
Firstly, it is crucial to verify that your backup power source can deliver sufficient energy. Many portable electric generators cannot provide the necessary minimum of 10 kilowatts, which means you will likely need to invest in a permanent generator or backup battery for your home.
These standby generators are capable of supplying enough power to run your entire household and charge your vehicle, but they tend to be large and costly. The investment for a home generator or backup battery typically ranges from $7,000 to $20,000.
If you are incorporating a home backup battery as part of a broader solar energy upgrade, the associated costs may be more manageable due to long-term savings on energy. However, this still represents a significant initial expenditure that not all electric vehicle owners may be ready to undertake.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that you possess the appropriate generator or battery and adapter to safely charge your electric vehicle. For example, Teslas require a True Sine Wave electrical output to prevent battery damage.
Always consult the documentation for both your vehicle and your backup power source before attempting to connect them.
Portability Is the Biggest Challenge When Charging an EV with a Generator
While having a high-capacity generator ensures your EV can be charged during emergencies or in remote areas, the size and weight can make transportation a real challenge. Large units that provide enough wattage for efficient charging are often bulky, requiring wheels or additional equipment to move.
Choosing the best generator to charge an EV means balancing power output with portability. Compact inverter generators can be easier to transport but may require more frequent refueling, while heavy-duty models deliver faster charging at the cost of mobility. Understanding your travel habits and charging needs is key to finding the right fit.
Portability presents a significant challenge, and a home battery backup may not be your only or primary concern. Deloitte’s 2022 Global Automotive Consumer Study indicates that range anxiety remains the primary obstacle for U.S. consumers considering a transition to electric vehicles (EVs).
For those concerned about accessing a charging station when necessary, the idea of carrying a backup battery or generator for recharging may arise. However, this presents a significant challenge.
Developing a backup power source that is compact enough to fit in a trunk while also providing a substantial charge is inherently difficult. Currently, one notable solution available is the ZipCharge Go.
Method 4: ZipCharge Go: A Portable Power Bank for Electric Vehicles
If the thought of using a gas-powered generator to charge your electric vehicle is unappealing, the ZipCharge Go could be a more suitable alternative. Set to officially launch in late 2022, this portable battery backup claims to offer 20-40 miles of range with a charging time of 30-60 minutes. It is compatible with any EV equipped with a Type 2 charging socket.
Although pricing details are not yet confirmed, it is anticipated to be subscription-based, costing approximately $68 per month. As more consumers enter the EV market, additional options like this will likely become available.
When Does Backup Power Make Sense for EVs?
With the right inverter generator and proper setup, you can restore enough battery power to keep moving until you reach a more permanent charging source.
That said, safety and compatibility are crucial. Not all generators can deliver the stable, continuous power EVs require, and using an incorrect setup may damage your vehicle’s battery system.
While some drivers ask, “Can you charge an electric car with a generator while driving?”, the answer is generally no—it’s neither safe nor supported by most EV manufacturers. However, when stationary and properly connected, a generator can be a valuable backup tool in your EV preparedness plan.
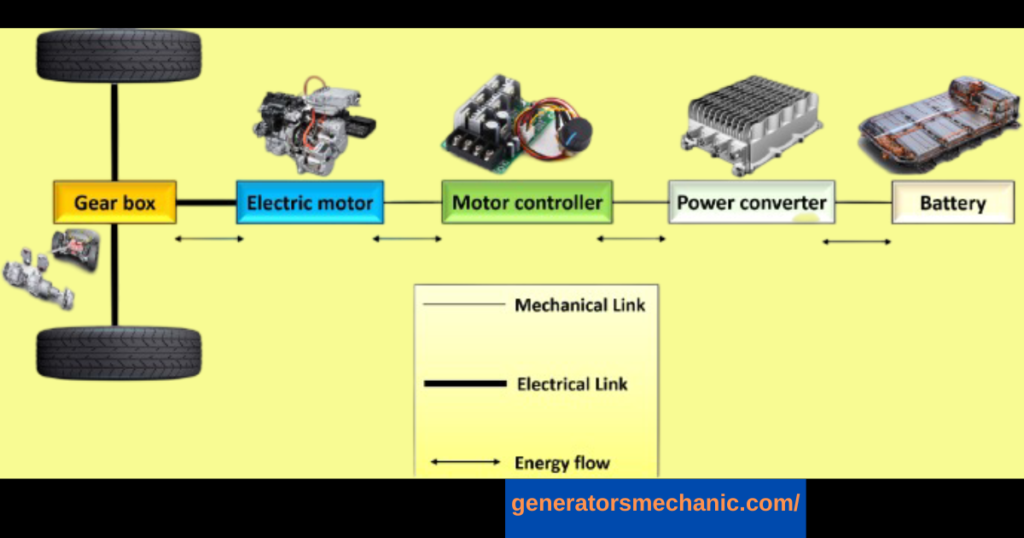
Range anxiety and concerns regarding charging remain significant issues for many individuals who currently own or are contemplating the purchase of an electric vehicle (EV). To address these apprehensions, one can explore methods to charge their electric car using a generator or a backup battery.
Nevertheless, these alternative power sources entail additional expenses and may involve the inconvenient reality of utilizing gasoline to charge your EV. As the charging infrastructure continues to develop, more opportunities for on-the-go charging will likely emerge, potentially reducing these concerns.
If you are considering backup power solutions for your EV, it is essential to thoroughly investigate your options and understand your vehicle’s specifications. Take the time to evaluate your decision carefully before making a purchase.
Conclusions:
Charging electric car with Honda generator car with a generator is a practical solution in situations where traditional charging stations are unavailable, such as during power outages or in remote areas. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the generator provides sufficient power output and operates efficiently to avoid potential damage to the car’s battery or charging system.
Opting for a portable, inverter-style generator is often the best choice for clean and stable power delivery. While this method offers flexibility, it should be considered a temporary solution rather than a primary charging method. Always prioritize safety and follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure a smooth and reliable charging process.
FAQs:
Can you charge Chinese electric car with generator
Yes, you can charge a Chinese electric car with a generator, provided that the generator’s power output and voltage are compatible with the vehicle’s charging system. Many Chinese EV brands, such as BYD, NIO, and MG, support AC charging, which means a portable inverter generator can be used for emergency or off-grid charging
Can I charge a car battery with a generator?
A generator can indeed be utilized to charge a battery. This process generally includes the following steps: Generator Output: The generator generates electrical energy, typically in the form of alternating current (AC).
Why can’t electric cars charge themselves with a generator?
It is important to note that an electric vehicle cannot incorporate a generator for self-charging because such a generator would draw more energy from the system than it could return to the battery pack. Additionally, the vehicle’s design would need to accommodate the extra equipment.
How does fast a generator charge an EV?
Charging Levels: Level 1 (120V) provides approximately 5 miles of range per hour, Level 2 (240V) offers around 25 miles of range per hour, and Level 3 (DC Fast Charging) can deliver between 100 to 200 miles of range in just half an hour.
What size generator do I need to charge an electric car?
Power Output and Generator Size: Larger inverter generators that can produce a stable and clean power output of at least 7,500 watts are more suitable for charging EVs. While these units may be costly and bulky, they are essential for delivering sufficient power for effective charging.
Can you charge an electric car with a generator while driving?
In most cases, you cannot charge an electric car with a generator while driving, because EV charging systems are designed to operate only when the vehicle is parked for safety and electrical stability. Electric vehicles have built-in safety protocols that prevent charging during motion to avoid electrical hazards or system malfunctions