Can a Generator Power an Air Conditioner? Full Guide
When the temperature rises, an air conditioner becomes one of the most important appliances in any home. But what happens if there’s a power outage during a hot summer day? Many homeowners wonder whether a generator can keep their AC running.
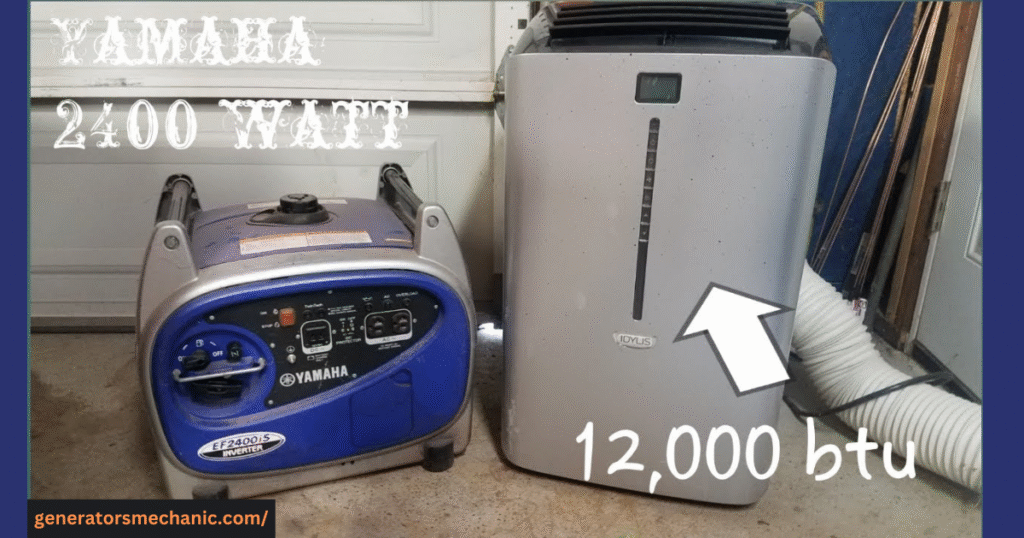

The simple answer is yes — but only if you choose the right generator size. Air conditioners require a higher amount of electricity to start and run smoothly, which means knowing what size generator to run an air conditioner is essential. By understanding your AC’s power needs and matching them with the right generator capacity, you can stay cool and comfortable even during unexpected blackouts.
Air conditioners make hot days bearable, but what if you lose electricity during the summer? That’s when a generator becomes a lifesaver. But here’s the big question many homeowners ask: Can a generator power an air conditioner safely and efficiently? The answer depends on the type of AC you own and the generator you use. Let’s break it down step by step.
Understanding the Power Needs of an Air Conditioner
Air conditioners are among the most power-hungry appliances in any home. To determine whether a generator can handle your AC, you first need to understand its power requirements. Every air conditioner has two main requirements: starting watts and running watts. Starting watts are the extra power required by the compressor to kick on, while running watts are the lower amount of electricity required to keep the unit operating.

For example, a small window unit may only need around 500 to 1,500 running watts, while a larger 1.5-ton split AC can require 2,000 to 3,500 watts. Bigger systems like central air conditioning can easily demand 5,000 watts or more, especially during startup. This is why knowing your AC’s exact wattage is essential before selecting a generator.
A common question people ask is, “Will a 7500-watt generator run my air conditioner?” In most cases, the answer is yes — a 7,500-watt generator is powerful enough to run a medium-to-large central AC unit and still leave room for some additional appliances. However, the final answer always depends on your AC’s tonnage and startup load. Having a generator with slightly more capacity than your AC requires is always a safer choice to avoid overloads.
Wattage requirements of different AC types
Not all air conditioners consume the same amount of power. For example:
- A small window AC (5,000–10,000 BTU) usually needs around 500–1,500 watts.
- A 1.5-ton split AC may need 2,000–3,500 watts.
- A central AC system can require 5,000 watts or more.
Starting watts vs running watts explained
Air conditioners often require extra power to start, known as starting watts. Once running, they use less power, known as running watts. For instance, a unit might run on 1,200 watts but need 2,000 watts to start.
Why do ACs need more power to start
The compressor inside an AC takes a sudden surge of electricity when it kicks in. That’s why choosing the right generator size is important — otherwise, your AC won’t start properly.
Can a Generator Run an Air Conditioner Safely?
Yes, a generator can run an air conditioner safely, but only if the generator is sized correctly and used with the right setup. Air conditioners draw a large amount of power during startup, which means the generator must have enough starting watts and running watts capacity to handle the load. Using an undersized generator can cause voltage drops, tripped breakers, or even damage to your AC’s compressor.
For example, many homeowners ask, “Will a 10,000-watt generator run a 4-ton air conditioner?” In most cases, yes — a 10,000-watt generator has enough power to start and run a 4-ton AC unit. However, this assumes the generator is dedicated mainly to the AC and not overloaded with other appliances at the same time. To ensure safe operation, it’s always a good idea to leave some extra wattage capacity, use a transfer switch, and keep your generator well-maintained.
Matching generator size with AC power needs
Yes, a generator can run an AC, but only if it has the right capacity. For example, a 3,500-watt generator is usually enough for a medium-sized split AC.
Common generator wattages that work with AC units
- 2,000W generator → Small window AC
- 3,500–5,000W generator → 1–1.5 ton split AC
- 7,500W+ generator → Central AC
Risks of using an undersized generator
If your generator is too small, it may overload, causing damage to both the generator and the air conditioner. It could also trip breakers or shut down unexpectedly.
Best Generator Types for Running an Air Conditioner
When it comes to powering an air conditioner with a generator, not all generator types are created equal. The best choice usually depends on the size of your AC unit and your overall power requirements.

Portable generators are the most common option for small window or split ACs. They are affordable and easy to move around, but may struggle with larger air conditioning systems.
Inverter generators are another excellent choice, especially if you’re running smaller to mid-sized ACs. They provide stable and clean electricity, making them safe for sensitive electronics as well as air conditioners. On top of that, they’re quieter and more fuel-efficient, which makes them ideal for home use or camping trips.
For larger central AC units, a standby generator is the most reliable option. These are permanently installed outside your home and can handle the heavy load of multiple appliances running at once.
Now, many people also ask, “How many ACs can run on a 1.5 kVA generator?” The reality is that a 1.5 kVA generator is too small to run more than a very small window AC or maybe a single fan and a few lights. Air conditioners require high starting wattage, so a generator of this size won’t be able to handle medium or large ACs. If you want to run multiple AC units, you’ll need a much higher capacity generator, usually 5 kVA or above.
In short, the right generator type depends on your AC’s wattage needs — from portable units for small ACs to heavy-duty standby generators for central cooling systems.
Portable generators
These are handy for small windows or portable ACs. They’re affordable but may not handle large appliances.
Inverter generators
Great for running smaller ACs safely. They are quieter, fuel-efficient, and stable, making them ideal for sensitive electronics and camping.
Standby generators
These are permanently installed and can handle whole-house loads, including central AC systems. They’re expensive but the most reliable option.
Factors to Consider Before Using a Generator for AC
When planning to use a generator to run an air conditioner and refrigerator at the same time, you need to think beyond just wattage numbers. The first and most important factor is the generator’s capacity. Both appliances have high starting watt requirements, so your generator must have enough surge power to handle the initial load. A unit that is too small may trip, shut down, or even damage your appliances.

Another key point is the fuel type and runtime. Gasoline, propane, and diesel generators all have different fuel efficiencies and costs. If you’re expecting long power outages, choosing a generator with a larger fuel tank or dual-fuel capability can save you from frequent refueling.
You should also consider power quality. Inverter generators provide stable and clean electricity, which is safer for modern AC compressors and refrigerators that often include sensitive electronics. Noise levels, portability, and proper ventilation are additional factors that affect everyday use and comfort.
Finally, never ignore safety precautions. Always use heavy-duty cords, place the generator outdoors to prevent carbon monoxide buildup, and avoid overloading it with too many devices. By carefully considering these factors, you’ll ensure that both your air conditioner and refrigerator run smoothly and safely on generator power.
Fuel type and runtime
Generators can run on gasoline, propane, or diesel. Propane burns cleaner, while diesel provides longer runtime. Always calculate fuel needs before relying on a generator.
Noise levels and placement
Some generators, especially conventional ones, can be very noisy. If you plan to use it at night, an inverter generator may be the better choice.
Safety concerns
Running a generator indoors or in closed spaces can cause carbon monoxide poisoning. Always place it outdoors in a well-ventilated area. Overloading should also be avoided to keep your AC and generator safe.
How to Calculate the Right Generator Size for Your AC
Choosing the right generator size for your air conditioner is all about understanding how much power your unit actually needs. Every AC has two important numbers: running watts (the power it uses while operating) and starting watts (the extra power needed to kick-start the compressor). To calculate the correct generator size, check your AC’s specification label or manual, note the running watts, and then add 20–30% more to cover the startup surge.
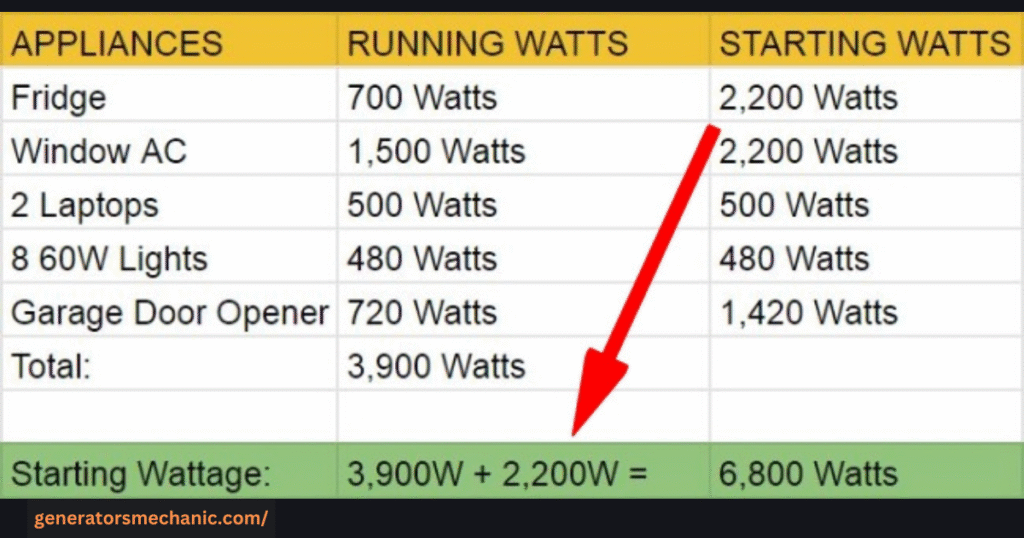
For example, if you’re wondering what size generator to run a 12,000 BTU air conditioner, you’ll usually need around 2,000–2,500 running watts and up to 3,000 starting watts. In this case, a generator with at least 3,500 watts of capacity would be a safe choice, giving you extra power to prevent overload. Always aim for a generator slightly larger than the minimum requirement — this not only keeps your AC running smoothly but also protects your generator from strain and extends its lifespan.
Step-by-step method to calculate watts
- Check your AC’s nameplate for running watts.
- Add at least 20–30% extra wattage for startup load.
- Match it with your generator’s rated and surge power capacity.
Example calculation for a 1.5-ton AC
If your AC requires 1,500 running watts and 2,500 starting watts, your generator should be at least 3,000 watts to run it comfortably.
Why extra wattage capacity matters
Having extra wattage prevents strain on your generator, improves efficiency, and extends both your ACs and your generator’s lifespan.
Practical Tips for Running an AC on a Generator
If you’re wondering how to run an AC on a generator without issues, the key is to balance power, safety, and maintenance. First, make sure your generator has enough capacity to handle the starting and running watts of your air conditioner. Using a soft starter can also reduce the initial surge, making it easier on your generator. Always place the generator in a well-ventilated outdoor area to avoid carbon monoxide buildup.

For wiring, use heavy-duty cords or a transfer switch instead of basic extension cables to ensure a stable power flow. Finally, don’t forget regular maintenance — changing the oil, checking fuel, and cleaning air filters will help both your generator and AC run smoothly. With these simple tips, you can enjoy cool air during power outages without stressing your equipment.
Use a soft starter
A soft starter reduces the initial surge load, making it easier for your generator to handle AC startup.
Maintain proper ventilation and wiring
Always use heavy-duty extension cords and ensure your generator has enough airflow to prevent overheating.
Regular maintenance
Both the AC and generator need timely servicing. Clean filters, change oil, and check wiring regularly for safe operation.
Final Thoughts: Is Running an Air Conditioner on a Generator Worth It?
Running an air conditioner on a generator can definitely be worth it, especially during power outages or when you’re in areas with unreliable electricity. The key is choosing the right size generator that matches your AC’s starting and running watts. For smaller units, a portable or inverter generator works well, while central air systems often need a standby generator.
To make things easier on your equipment, many homeowners use an AC soft start for generator setups. A soft start reduces the heavy surge of power that air conditioners need at startup, allowing your generator to run more efficiently and with less stress. In the end, the investment is worth it if comfort, safety, and peace of mind during hot summer days are your top priorities.
The short answer: Yes, a generator can power an air conditioner — but only if it’s sized correctly. For small windows or split units, a portable or inverter generator can do the job. For central ACs, a standby generator is the best option. Always calculate your power needs, use safety precautions, and invest in the right generator for a stress-free cooling experience.
Common FAQs About Generators and Air Conditioners:
Can a 5000-watt generator run a central AC?
Mostly no. Central ACs usually need 7,500 watts or more.
Is it safe to run an AC on an inverter generator?
Yes, as long as the inverter generator has enough wattage capacity.
How long can I run an AC on a portable generator?
That depends on the generator’s fuel tank size. Usually 6–12 hours per refuel.
Do I need a transfer switch to power my AC with a generator?
For home ACs, yes. A transfer switch ensures a safe and legal connection without back-feeding into the grid.
Can a portable generator run a window AC?
Yes, most portable generators with 2,000–3,000 watts can run a small window AC unit. Always check both starting and running watts before use.
Is it safe to connect an air conditioner directly to a generator?
It’s safe only if the generator is sized correctly and connected using a transfer switch or heavy-duty cord. A wrong setup can damage appliances.
How big a generator do I need to run a 1.5-ton AC?
A 1.5-ton AC usually needs 3,000–3,500 watts to run smoothly. Choose a generator with at least 20% more wattage for safety.
Can an inverter generator run an AC?
Yes, inverter generators can run small to medium-sized ACs if they provide enough wattage. They’re quieter and safer for electronics, too.
How long can I run my air conditioner on a generator?
This depends on fuel tank size. Portable generators typically run 6–12 hours per refuel, while standby generators can run much longer.
Do I need a soft starter for my AC when using a generator?
A soft starter isn’t mandatory, but it reduces the initial power surge and makes it easier for smaller generators to handle AC startup.
What size generator do I need to run an air conditioner?
The generator size you need depends on your AC unit’s wattage. A small window AC may only need a 2,000–3,000-watt generator, while a 1.5-ton split AC typically requires at least 3,500 watts. Larger central AC units (3–5 tons) may need 7,500 watts or more. Always check both starting watts and running watts of your AC before choosing a generator.
Can a generator damage an AC unit?
Yes, if the generator is undersized or produces unstable power, it can damage an air conditioner. Voltage fluctuations and power surges may harm the compressor or electronics. To avoid this, choose a properly sized generator and, if possible, use an inverter generator or add a voltage stabilizer for extra protection.
Can a 10,000-watt generator run a 3-ton AC unit?
Most 3-ton AC units need around 6,000–7,500 running watts and even more during startup. A 10,000-watt generator should be sufficient to power a 3-ton AC comfortably, as long as you’re not running too many other heavy appliances at the same time.
Do generators produce AC power?
Yes, most household generators produce AC (alternating current) power, which is the same type of electricity you get from the utility grid. This makes them suitable for running air conditioners, lights, refrigerators, and other home appliances.
Will a 12,000-watt generator run a 5-ton AC unit?
A 5-ton central AC typically requires between 10,000–12,000 watts just for itself, especially at startup. A 12,000-watt generator may be able to run it, but it will likely be at full capacity, leaving little room for other appliances. For safer operation, it’s better to have a generator with some extra wattage overhead.
Can a generator damage an AC unit?
Yes, it can — particularly if the generator is too small or produces “dirty power” with unstable voltage. This can stress the compressor and shorten your AC’s lifespan. To avoid damage, always match the right generator size to your AC’s requirements and use safe connection methods.
Can I run my whole house on a 12,000-watt generator?
In many cases, yes. A 12,000-watt generator is powerful enough to run essential appliances like refrigerators, lights, fans, and even a medium-to-large AC unit. However, whether it can run your entire home depends on your total power consumption. Homes with electric water heaters, central heating, or multiple heavy appliances may require more than 12,000 watts.